a coating, which reduces the specular reflectance of a surface by increasing the diffuse reflectance from that surface
Table of contents
a coating, which reduces the specular reflectance of a surface by increasing the diffuse reflectance from that surface
We have already reported on Gorilla Glass in various blog posts. If you search for the term on the Internet, you will also notice that many suppliers excel in using Corning's Gorilla Glass in their products. It is no secret that many smartphones, tablet PCs or large flat screens attach the glass to protect it from the outside world. But what makes Gorilla Glass different from other glass?
We have written several times about the US company Corning, Inc., based in Corning, New York, which produces glass, ceramics and related materials for industrial and scientific applications. Among other things, one of Corning's best-known products is Gorilla Glass, which was launched in 2007. It is characterized by high resistance to breakage and scratches.
The car manufacturer Range Rover not only equips the center console of its cars with touchscreen technologies, but also uses touch displays for other functions. An app from the manufacturer now makes it possible for the touchscreen of a smartphone to act as a remote control for its new Range Rover Sport off-road vehicle.
Graphene is a chemical relative of diamonds, coal or the graphite of pencil leads. It is one of the hardest and most resilient materials in the world. With only one atomic layer (less than a millionth of a millimeter thick), it is also one of the thinnest materials in the universe.
Linear thermal expansion is a critical factor to consider in environments with wide temperature requirements, as it can cause problems due to different thermal expansion coefficients of touch screen materials or the bezel structure. Different coefficients of thermal expansion can be defined for a substance, such as linear thermal expansion (LTE), area thermal expansion (ATE), or volumetric thermal expansion (VTE). Some substances expand when cooled, such as freezing water, and have negative thermal expansion coefficients.
Glass is strengthened by two methods: heat treating and chemical strengthening, where the glass is subjected to a special heat treatment and cooled, and tempered glass, which is made by heating annealed glass uniformly and cooling it faster than heat-strengthened glass. The main reasons to strengthen glass are to increase wind load, increase impact resistance, and combat thermal stress.
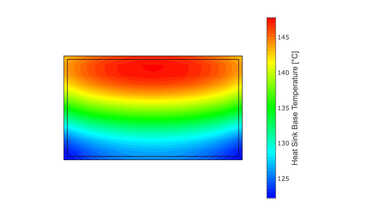
Explore the critical reasons behind the premature failure of outdoor touch screens designed for extreme temperatures and sunlight at Interelectronix. Our deep dive into passive cooling limitations, the impact of solar load, and the shortcomings of climate chamber testing reveals essential insights. Learn how active cooling, real-world scenario testing, and our 25 years of experience can enhance the durability and reliability of your outdoor screens.
Explore our comprehensive guide on setting up Raspberry Pi OS, cross-compiling Qt 6.8 for Raspberry Compute Module 4 on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS, and configuring Qt Creator for efficient development. Our tutorials cover installation, updating to the latest software versions, and building a cross-compiler toolchain. Whether you're working on a native computer or a virtual machine, our step-by-step instructions ensure a smooth setup for your Raspberry Pi projects.

Navigating hazardous environments is challenging, especially when balancing compliance with operational efficiency. At Interelectronix, we’ve seen firsthand how crucial the IEC 60079 series is for ensuring safety in explosive atmospheres. Understanding these standards isn’t optional—it’s a vital part of protecting your team and equipment. Let’s explore what this means for your operations.
Impactinator® IK10 glass offers unparalleled impact resistance, making it a superior choice for applications requiring exceptional durability. This innovative family of special glasses has revolutionized the industry, enabling glass solutions previously deemed impossible.
Designed for touchscreen and protective glass applications, Impactinator® glass meets the stringent safety and vandalism standards of EN/IEC62262 IK10 and IK11. It excels in situations where impact resistance, weight reduction, image quality, and reliability are critical.
Choose Impactinator® glass for robust and dependable performance in demanding environments. Experience the future of glass technology with our cutting-edge solutions that ensure maximum protection and efficiency.